[Warning: Long read.]
My personal experience of having many good friends among both men and women is leading me to believe that differences between the two genders are real, but that their nature is very complex and that any attempt to characterize one versus the other ends up in traits that span some of both genders’ populations. No matter what profile is devised with the intention to characterize what a man’s trademark traits are, there will be women I know who excel at some of them, and, equally, I can think of men who excel at traits that would be attributed to the archetypal woman.
Claims that women are more intuitive while men are more rational have always struck me as simplistic and reductive in terms of their predictive capacity in the face of meeting a new person of either gender, and – more importantly, I have found them to be unhelpful, or even obstructive, when it comes to building relationships. Yet, the view of resolving the question about the differences between men and women by means of two list of ‘typical’ traits is very popular, as can also be seen from best-sellers like “Men are from Mars, Women are from Venus” (the first book I read that compelled me to write a review on Amazon :).
To counter this trend, I would like to sketch out my understanding of how men and women compare, and do so from two perspectives: the first one being science (both neuroscience and psychology) and the second one religion (specifically Christianity, and even more specifically Catholic exegesis, the Theology of the Body of St. John Paul II and the intellectual visions of the Servant of God, Chiara Lubich).
From the perspective of science, there is a growing body of work on quantifying both the neurological/physiological and psychological differences between men and women, where certain physical as well as behavioral differences have been measured repeatedly and for which evidence is mounting.
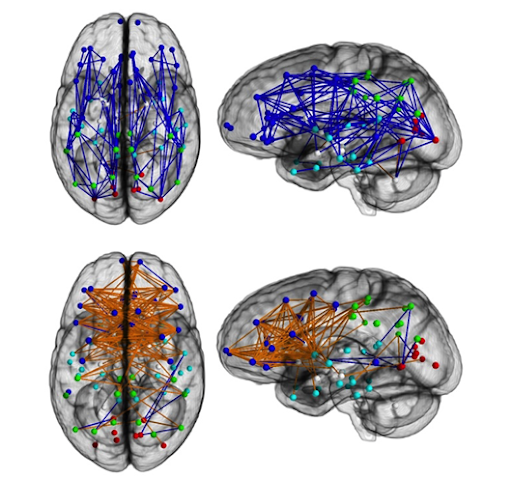
On the neurological and physiological side, there is strong evidence (obtained by a team from Oxford and Cambridge, who pooled together 126 studies, involving 43 000 subjects) to show that the brains of men are between 8% and 13% larger in volume than those of women. There is also evidence for there being significant differences between the relative volumes and densities of different regions in the brain between men and women. A recent example here is the work of Nopoulos et al. from the University of Iowa, who used functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) to study the ventral prefrontal cortex (VPC), a region involved in social cognition and interpersonal judgment. The findings, based on 30 men and 30 women, showed a relatively larger volume of this region in women, by 10%. In other words, relative to the total volume of a brain, the VPC region is 10% larger in women. Finally, there are not only volumetric differences between the brains of men and women, but also morphological ones. Here the most well-known, recent study is by Ingalhalikar et al., where the brains of 949 subjects (428 male and 521 female) were studied in terms of the nature of neural connections (connectome maps) between and within brain hemispheres (using diffusion tensor imaging). The results showed a systematic difference where male brains displayed a greater degree of intra-hemispherical synaptic connections (see top of following figure), while female brains had more prevalent inter-hemispherical links (see bottom of following figure). Interestingly, the authors of this study refer to the differences between the connectome maps of males and females as being a “complementarity” that makes them particularly suitable for collaboration …
While there is strong evidence for systematic physiological differences between male and female brains, the question of what their consequences are remains far less clearly understood. E.g., taking the question of intelligence, there are studies whose results support all three of the possible outcomes: that there is no statistically significant difference, that men are more intelligent, or that women are more intelligent on average (e.g., see pp. 72 of the following paper). Even in the cases where a difference is shown, it tends to be small: 2-4 points in terms of the well known IQ test, and whether it is men or women who come out ahead depends on the specific test used. E.g., in a study involving 6780 subjects from Brazil, women came out ahead by 2 IQ points using Cambraia’s Attention Test, while men did better in Raven’s Standard Progressive Matrices test – by 1.8 IQ points. Similarly the behavioral consequences, from the perspective of differences between the sexes, of the VPC differences measured by Nopoulos et al., present a complex picture. There, no significant differences were found between men and women in terms of performing the Interpersonal Perception Task, which tests a subject’s ability to understand different types of social interaction. However, when the subjects were asked to complete a Personal Attributes Questionnaire (answering questions that lead to the subject’s self-perception in terms of two scales: “instrumentality” and “expressivity”, which are commonly taken to stand for masculinity and femininity and are used as a measure of gender identity), the resulting scores displayed strong correlation with the Interpersonal Perception Task outcomes.
The point of the above examples taken from recent findings in neuroscience and psychology, from studies that explore the differences between men and women, is to illustrate the complexity of the results obtained to date. On the one hand there is strong evidence for biological differences between male and female subjects, while on the other hand the specific nature of the differences and their impact on psychological traits or inclinations is complex and does not neatly divide along lines of a subject’s sex. While nature differs on average, an individual’s characteristics make them different from their sex’s average, with nurture and society further contributing to there being a continuum of states instead of a binary categorization of abilities, preferences, or traits. In my opinion, the psychology of personality, as opposed to that of gender, is a better means for understanding how one individual may differ from another in terms of their preferences and inclinations, which in turn can facilitate building mutually-fulfilling relationships.1
Turning to how the differences between men and women are understood in the context of Christianity, I would like to highlight three perspectives, as already mentioned at the beginning of this post.
First, there is St. John Paul II’s Theology of the Body, as set out in his “Men and Women He Created Them,” which I have already written about at length here. The only insight I’d like to point to here is John Paul II’s insistence on men and women being created “in the image of God” intrinsically referring to the communion of Persons in the Trinity. He makes this clear by saying that “man2 became the image of God not only through his own humanity, but also through the communion of persons, which man and woman form from the very beginning.” And it is in this context that the differences between men and women have a specific purpose, which is that these “two reciprocally completing ways of “being a body” [… are] complementary dimensions of self-knowledge and self-determination.” This in turn leads John Paul II to saying that a person’s “sex expresses an ever-new surpassing of the limit of man’s solitude [… and] always implies that in a certain way one takes upon oneself the solitude of the body of the second “I” as one’s own.” Men and women are different and complementary, but in profound, existential ways rather than as reducible to a trivial set of typical features or traits.
Second, the New Testament is rich in portraying different roles played by men versus women in the context of Jesus’ mission on Earth. Here Damiano Marzotto’s “Pietro e Maddalena” (mentioned by Pope Francis as being on his reading list), does a superb job of analyzing what these roles are in the Gospels, as a first step towards understanding how women could play the prominent role that they need to have in the Church, which they lack today. Marzotto summarizes his findings by first pointing out a greater propensity in women for welcoming Jesus’ teaching and making themselves available for a deepening and contemplation of his message (with men then acting on what the women understood). Mary’s keeping the events surrounding Jesus’ birth and “reflecting on them in her heart” (Luke 2:19) illustrates this very clearly. This places women in a position of welcoming novelty, of taking risks and of stepping out of line – traits not commonly associated with women in first century Palestine. The women of the Gospel, while having some common features, very much break the mold of societal stereotypes – another argument against characterizing men and women by sets of static, opposed features. The second aspect that Marzotto identifies in the women of the Gospel is an ability to anticipate Jesus’ actions and to provoke him or the apostles to action. Mary’s intervention at the wedding in Cana (John 2:1-12), or Mary Magdalene going to the apostles after meeting the risen Christ (John 20:1-3) are good examples here. Finally, Marzotto also argues that women have been responsible for a broadening of Jesus’ mission, for a greater universality of who it is addressed to. Here the woman suffering from hemorrhage (Mark 5:25-34), the Samaritan woman (John 4:4-42), the Canaanite woman (Matthew 15:21-28), or the widow of Nain (Luke 7:11-17) are great examples.
Third, the Servant of God, Chiara Lubich, in her intellectual visions (like those of Sts. Teresa of Ávila and Ignatius) during the summer of 1949 (referred to as the Paradise ’49), prefigures St. John Paul II’s interpreting the relationship between men and women from the perspective of the Trinity. As Giuseppe Maria Zanghí puts it, “this means that a meeting between the two “differences” requires, in each one of the two, a fullness of being: their synthesis is possible […] because, already before the two meet, each one of them is complete in themselves. Every form of weakness, every temptation of “subjection”, is overcome. […] True unity between man and woman can be achieved if each of the two realities is fulfilled in itself.” During her visions in 1949, Lubich recounts the following insight:
“The perfect man has the woman in him: he contains in his strength all of feminine sweetness, in his directness all of a woman’s suppleness. His character is unitarian, closed and severe like unity. But, if he is perfect (unitarian), he contains in himself the Trinity, who is a woman that is all open, caressing, loving. So the woman too, if she is perfect, encloses her open character in self-restraint that is reminiscent of the Madonna. She is man. Trinity in Unity.” (Paradise ’49, 1319-1320)3
The relationship between men and women, as understood also by Lubich in her mystical vision, is one of unity in distinction and distinction in unity, which is love. To reduce it only to distinction, and to a simplistic binary one at that, is to deny the Trinitarian image in which both men and women were made, and it is also to distort the complex and deeply beautiful picture that science is in the process of understanding as we speak.
[UPDATE on 17 November 2014:] Today Pope Francis opened a symposium on precisely the subject of how men and women relate, entitled “The Complementarity of Man and Woman in Marriage,” during which he had the following to say about the nature of differences between the sexes:
“Christians find [the] deepest meaning [of complementarity] in the first Letter to the Corinthians where Saint Paul tells us that the Spirit has endowed each of us with different gifts so that-just as the human body’s members work together for the good of the whole-everyone’s gifts can work together for the benefit of each. (cf. 1 Cor. 12). To reflect upon “complementarity” is nothing less than to ponder the dynamic harmonies at the heart of all Creation. […]
When we speak of complementarity between man and woman in this context, let us not confuse that term with the simplistic idea that all the roles and relations of the two sexes are fixed in a single, static pattern. Complementarity will take many forms as each man and woman brings his or her distinctive contributions to their marriage and to the formation of their children — his or her personal richness, personal charisma.”
1 But, we’ll have to leave that for another time …
2 “Man” here meaning the human person (as is clear from the context of the original text).
3 Apologies for the crude translation, the Italian original can be found in Zanghí’s “Leggendo un carisma” on pp. 149-150.



