The hallmarks of the scientific method include its basis in empirical evidence and its reliance on repeatability for the sake of verifying or falsifying hypotheses accounting for and predicting observations that can be aided by measurement. An aspect of the above that has interested me for a while now has been the nature of repeatability (or reproducibility), which certainly does make good intuitive sense, but where I had questions about whether some other principle couldn’t be used instead to form an equally consistent method of enquiry. Essentially, I was wondering to what extent the scientific method, as anchored in repeatability, allowed for a formalistic reading (like mathematics does – in contrast with conceiving of it as a form of realism).
The breakthrough for me came when my bestie NP wrote a soon to be published article to stimulate dialogue between science and faith and listed the following two of the assumptions of science: namely, that “the universe is intelligible […] and that it has a rational structure.” While both of these may sound self-evident and be taken for granted, having them called out made me think more carefully about intelligibility. What is it that renders an event or entity intelligible and how does a successful understanding demonstrate itself? Especially the latter is a staple of epistemology and the philosophy of science and I don’t mean to review the literature on explanatory power or models of scientific explanation like the deductive-nomological one here. Instead, I’d like to focus on the role of repeatability and to argue that it is necessary not only for science but that it is inextricable from any expression of reason.
The repeatability of events, of the meaning of concepts and of the modes of reasoning is essential to rationality. If such recurrence and persistence of relationships and states did not exist, then each event would be a one-off and it would be impossible to conceive of it using human reason. Language would not exist since words would at most be labels for individual entities and the games it relies on would be impossible too since they require regularity and repetition. Understanding of any kind would also be impossible since reflection and either deductive or inductive modes of analysis would have a sole window of opportunity in which to relate to an event or entity. There would be no laws, rules, regularities or even statistics, since everything that would be, would be a unique, a one-of-a-kind. This necessity of repeatability and its being a constituent of rationality are also expressed in Einstein’s definition of “Insanity: doing the same thing over and over again and expecting different results.”
In science, the insistence on repeatability is then anything but arbitrary and instead becomes an expression of its rationality. It can even be seen as closing the loop that starts with the assumption of the repeatability and regularity of phenomena by requiring of a theory to be repeatably applicable to their recurrences to merit the status of scientific. In other words, the requirement of repeatability in science mirrors the assumption of the repeatability in nature to which it strives to correspond.1
With the above thoughts in mind, and having read and hugely admired John Paul II‘s analysis of Genesis from the perspective of the human person, I proceeded to attempt an imitation from the point of view of science, knowing full well that it could at best be as if seen through a mirror, darkly. Nonetheless, I believe that I have found – to me – surprising traces of the scientific method in the first chapter of the Bible.2 Before making these explicit, I would like to emphasize that I am not looking for a justification of science in the Bible (it is solidly derived from reason alone as sketched out above as well) and neither am I setting out to anachronistically twist the Genesis text to fit contemporary thought (although I am necessarily looking at it from a contemporary perspective). Instead, inspired by John Paul II, I am attempting to look for the roots of what today is the scientific method and I would have been unperturbed even if I had found no traces of it there.
The first thing that struck me when re-reading Genesis 1 over the weekend is its use of the following, exact sentence to conclude the account of each “day” of creation: “Evening came, and morning followed—the [n-th] day.” (verses 5, 8, 13, 19, 23 and 31). Instead of the creation myth3 being a single “poof” event or a random sequence of entities popping into existence (à la Eddie Izzard’s great sketch4), it has a repeating structure as its backbone. Once set up on the first day (“God then separated the light from the darkness. God called the light “day,” and the darkness he called “night.”” 1:4-5), the alternation of day and night repeats itself and becomes subject to predictability and intelligibility.
The second feature of Genesis 1 that is worth noting in this attempt to trace the roots of science in the Torah is the repeated reference to visual observation. As early as verse 4, after the creation of light, we hear that “God saw that the light was good” and as far as the various translations and analyses I have seen, the term translated into English as “saw” does refer to ocular perception as opposed to just understanding in the abstract. Then, in verses 10 (after dry land is separated from water), 12 (after the introduction of vegetation), 18 (after the sky is populated), 21 (after fish and birds are created) and 25 (after animals living on land enter the scene) we are told repeatedly that “God saw that it was good.” From this perspective of visual perception, it is also worth noting that it is employed in a categorically different way once the two first humans are present.
Instead of vision only being a means for God to assess His own work, in His relationship with humans he calls them to use it as a source of evidence for His actions: “God also said: See, I give you every seed-bearing plant on all the earth and every tree that has seed-bearing fruit on it to be your food; and to all the wild animals, all the birds of the air, and all the living creatures that crawl on the earth, I give all the green plants for food.” (Genesis 1:29-30). In fact, the very last verse of Genesis 1 (verse 31), brings both visual observation and the repetitive, predictable nature of the universe together: “God looked at everything he had made, and found it very good. Evening came, and morning followed—the sixth day.”
What the above means to me is that Genesis, and therefore the whole of Judeo-Christian thought, is rooted in an account of creation that, albeit being in the form of a myth, has features that clearly contain two core aspects of the scientific method: repeatability and predictability on the one hand and sensory observation as a means of obtaining evidence on the other. While not a factual account of cosmogeny, Genesis nonetheless hints at how nature is to be approached also from the perspective of understanding it: that regularity can be expected and that the senses are a basis for engaging with it. Instead of being a source of superstition and confusion, the Bible to me is a source of gems that reinforce rather than oppose rationality.
1 I think it unlikely for this train of thought to be novel, so the absence of references is an expression of my ignorance rather than innovation. All I can offer here is the acknowledgement of Aristotle’s already realizing that “there is no science of the individual” (“If they are individual and not universal, real things will be just of the same number as the elements, and the elements will not be knowable.” Metaphysics XIII, 10).
2 I don’t wish to scare you off by setting out to link science directly to the Bible. Let me assure you that my intentions couldn’t be further from those who consider the universe to the 6000 years old or who run lunatic websites like answersingenesis.org (scarily that was the website that the vast majority of Google “science Genesis” searches point to). On the topic of answersingenesis.org, I was particularly struck by their attempt to distinguish between two flavors of science: historical (explaining past events) and operational (applied in the present for utilitarian ends). What the @#$%?!
3 I am using the term myth in the way in which John Paul II employed it: myth “does not refer to fictitious-fabulous content, but simply to an archaic way of expressing a deeper content.” (Man and Woman He Created Them
4 “So then God created the world, and on the first day he created light and air and fish and jam and soup and potatoes and haircuts and arguments and small things and rabbits and people with noses and jam – more jam, perhaps – and soot and flies and tobogganing and showers and toasters and grandmothers and, uh … Belgium. And the second day he created fire and water and eggnog and radiators and lights and Burma and things that go “urh” and … and Colonel Gaddafi and Arthur Negus. On the third day he probably got lists and said, “I can’t remember what I’ve invented now. I’ve just been ad-libbing so far.”” (Eddie Izzard, Glorious, 1997)









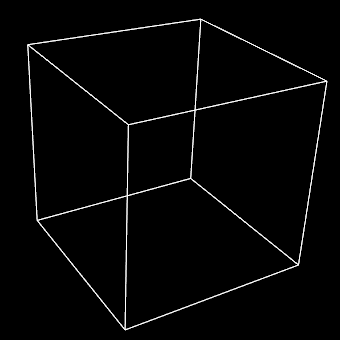 When you look at the above image, what do you see? Two triangles and five quadrangles, a cube or something else? Now, let’s turn to the following thought experiment:
When you look at the above image, what do you see? Two triangles and five quadrangles, a cube or something else? Now, let’s turn to the following thought experiment: